开放合作系列
-
Study of laboratory bubble columns by direct numerical simulation and multiphase VOF method
Abstract
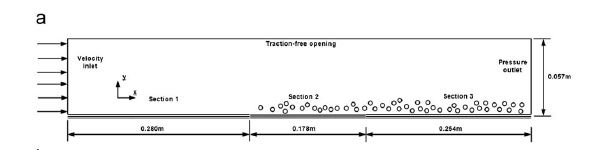
A rapidly increasing number of studies have been made on the modeling of bubble columns using computational fluid dynamics (CFD). In this work, we present a hybrid Eulerian-Eulerian (E-E) volume of fluid (E-E-VOF) method to simulate laboratory rectangle bubble columns with different superficial velocities. This method treats each phase under the E-E framework. Meanwhile, an interface compression term is added in the phase fraction equation to capture the large-scale interface. Quasi direct numerical simulation (quasi-DNS) with interface tracking and the classical E-E method are also employed as benchmark models. Our results show that the macroscopic features in the investigated laboratory bubble columns, such as the averaged phase fraction at different cross sections, the liquid velocities and the bubble plume period, predicted by the E-E-VOF, E-E method and quasi-DNS agree well with experimental data. Both the E-E-VOF and the quasi-DNS can predict the bubble swarm with large-scale interface. However, the quasi-DNS is highly computational resources demanding compared with the E-E-VOF method, which limits its application to industrial simulations.
Results
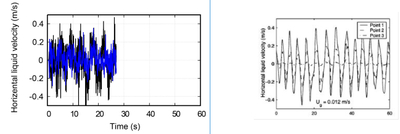
Left: Prediction of the horizental liquid velocity by the quasi-DNS (not finished yet!). Right: Prediction by the E-E method in the literature.Main References
- Díaz, M. E., Iranzo, A., Cuadra, D., Barbero, R., Montes, F. J., Galán, M. A. (2008). Numerical simulation of the gas–liquid flow in a laboratory scale bubble column: influence of bubble size distribution and non-drag forces. Chemical Engineering Journal, 139, 363-379.
- Li, D., Christian, H. (2017). Simulation of bubbly flows with special numerical treatments of the semi-conservative and fully conservative two-fluid model. Chemical Engineering Science, 174, 25-39.
Job:
- Data processing
- Test cases debugging and running
- Writing paper in English if you are willing to
Requirements:
- Knowledge of OpenFOAM.
- Background in bubble column or gas-liquid dispersion, otherwise you have no idea what to write in the Introduction part!
- Knowledge of VOF method, E-E method.
- Manuscript should be written in Latex. Our aim is top journals in chemical engineering.
Benefits:
- You can get around 30000 yuan bonus from your host (if you write the manuscript).
- You can use this paper to get promoted faster (if you write the manuscript).
- Another 10000 yuan from my side
- If I write the paper, I can support you 40000 yuan as well. However, I dont have much time to write. So I prefer you writing the paper and to be the first author.
Project duration
Since I have the raw results already. Manuscript should be completed in two months after you undertake this project. One month extension is tolerated, if necessary.
-
Simulation of the micro-bubble drag reduction by the Eulerian quadrature-based moments method
Abstract
The presence of near wall bubbles may reduce the skin friction drag. It can be simulated by the two-fluid model (TFM) coupled with the population balance model (PBM). One disadvantage of the TFM-PBM coupling is that the bubbles with different sizes are transported with identical velocities. In this work, the phenomenon of drag reduction by the injection of micro-bubbles into turbulent boundary layer was investigated by the four-way coupled Eulerian quadrature-based moments method (E-QBMM). In the E-QBMM, bubbles movement is controlled by the generalized population balance equation (GPBE). The GPBE is transformed to the moment transport equations and solved by the higher-order realizable finite volume scheme. Simulation results predicted by the E-QBMM are compared against experimental data in the literature. Our results show that the E-QBMM
Results

Main References
- Mohanarangam, K., Cheung, S. C. P., Tu, J. Y., Chen, L. (2009). Numerical simulation of micro-bubble drag reduction using population balance model. Ocean Engineering, 36, 863-872.
Job:
- Data processing
- Test cases debugging and running
- Writing paper in English if you are willing to
Requirements:
- Knowledge of OpenFOAM.
- Background in bubble drag reduction, otherwise you have no idea what to write in the Introduction part!
- Knowledge of E-E method, population balance model.
- Manuscript should be written in Latex. Our aim is top journals in ocean engineering.
Benefits:
- You can get around 30000 yuan bonus from your host (if you write the manuscript).
- You can use this paper to get promoted faster (if you write the manuscript).
- Another 10000 yuan from my side
- If I write the paper, I can support you 40000 yuan as well. However, I dont have much time to write. So I prefer you writing the paper and to be the first author.
Project duration
Since I have the raw results already. Manuscript should be completed in three months after you undertake this project. One month extension is tolerated, if necessary.
-
Simulations of gas-liquid dispersions by four-way coupled E-QBMM with aggregation and breakage processes
Abstract
Results
Main References
Job:
- Data processing
- Test cases debugging and running
- Writing paper in English if you are willing to
Requirements:
Benefits:
- You can get around 30000 yuan bonus from your host (if you write the manuscript).
- You can use this paper to get promoted faster (if you write the manuscript).
- Another 10000 yuan from my side
- If I write the paper, I can support you 40000 yuan as well. However, I dont have much time to write. So I prefer you writing the paper and to be the first author.
Project duration
